oceanography
Fundamental academic field encompassing everything from the atmosphere to the ocean (including the seafloor)

Marine biology
Academic area related to interactions between diverse marine organisms and the environment

Comprehensively study the basic sciences related to the ocean and marine life (physical, chemical, biological, geological) and develop it into science and technology for investigating, analyzing, conserving, and utilizing the marine environment and marine life. We aim to
School of Marine Life ScienceShinagawa Campus
School of Marine TechnologyEtchujima Campus
Graduate Schools
Graduate School of Marine Science and TechnologyShinagawa Etchujima Campus
By incorporating the ocean floor and geological systems into our existing strengths in education on the ocean, marine environment, and marine life, we will create a program that deals with the ocean in an integrated manner and provide education that meets international standards.
Utilizing the hands-on training in marine research and observation using training vessels, which is the most distinctive feature of our university's "Oceanology/Marine Environmental Studies" education, we will provide education that is superior to educational programs in other countries.
Based on basic and applied science related to assessment of the impact of human activities on the marine environment and environmental management and restoration, students select from the following two subject groups and study systematically and professionally.
In specialized subjects, students will study a wide range of basics about the principles and interactions of physical, chemical, biological, and geological phenomena in the hydrosphere, and will acquire basic “oceanography” that encompasses the entire ocean, or diverse marine life. Students focus on one of the two academic fields (specialized subject groups) of "Marine Biology", which deals with interactions between animals and the environment, and acquire specialized skills.
Fundamental academic field encompassing everything from the atmosphere to the ocean (including the seafloor)

Academic area related to interactions between diverse marine organisms and the environment

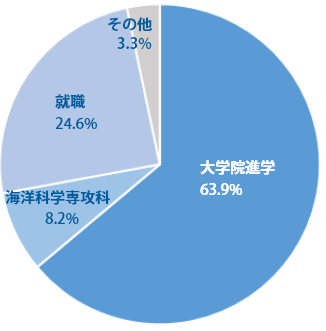
With the qualifications to be able to respond internationally at marine development sites based on environmental conservation, we are able to work in practical fields (basic design/construction, environmental impact assessment, consulting) at companies, national and local government agencies related to ocean utilization, resources and energy. ), develop human resources who can play an active role in basic research fields, and administrative fields.




Alpha Suiko Consultants, Enigmo, NTT Comware, Orix Aquarium, Japan Coast Guard, CLINKS, high school teachers, group meals, Fisheries Agency, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Toyo Signal Communications, Toyo Suisan, Toyo Reizo, Prefectural Fisheries Experiment Station, Prefectural Government Office and city and ward officials, National Federation of Fisheries Cooperatives, Nafco, BML Food Science, Miura Industries, Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance, Rinkai, etc.
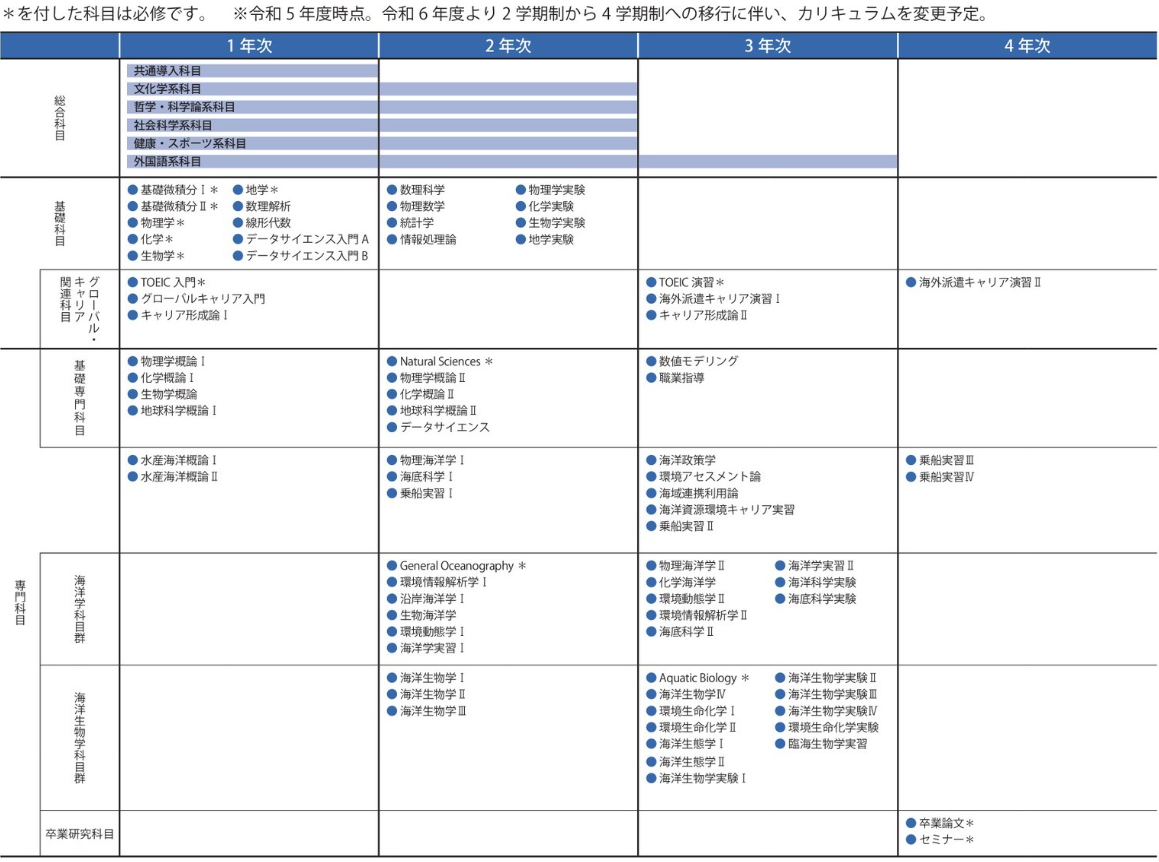
In the Department of Marine and Environmental Science, we offer ``General Subjects,'' ``Introductory Subjects,'' ``Basic Specialized Subjects,'' and ``Specialized Subjects,'' in order to help students acquire the four basic skills and abilities listed in ``2'' below. We will systematically organize ``subjects'' and ``global career-related subjects.'' Furthermore, in order to facilitate cross-disciplinary study of specialized subjects, we will organize content related to marine science, marine biology, and their boundary areas into ``specialized subjects.''
Class subjects are divided into ``general subjects,'' ``specialty introductory subjects,'' ``basic specialized subjects,'' ``specialized subjects,'' and ``global career-related subjects,'' with lectures and exercises. , conduct experiments and practical training.
(1)Specialized knowledgeIn all subjects, learning outcomes and achievement of goals are rigorously evaluated through exams, reports, presentations, etc.
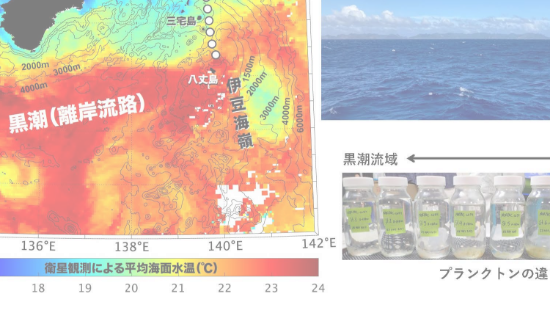
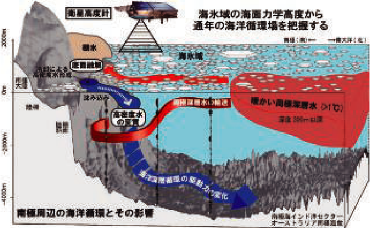
Marine environmental science is based on oceanography, which observes, analyzes and predicts various phenomena in the ocean, and marine biology, which analyzes the interaction between marine organisms and the environment, and develops this into science and technology for marine environment conservation and restoration. Education and research in accordance with curriculum policy. Specifically, we conduct physical, chemical, and geological observation and exploration of the ocean and seabed, investigation and research into diverse marine life (from microorganisms to cetaceans), and biotechnology for the conservation of marine life and the use of useful materials. We work on issues such as biochemistry, modeling and prediction of the effects of marine phenomena and human activities, and planning and implementing plans for conservation and restoration of the marine environment. We are looking for people who are interested in these issues and have the desire to acquire specialized knowledge, a rich international perspective and wide-ranging education, the ability to think and make decisions on their own, and practical skills that can be used in the field by the time they graduate, as stated in the diploma policy. .
Applicants must possess the necessary background and basic academic ability to receive a wide-ranging education in the natural sciences, especially basic academic ability in mathematics and science (any two of physics, chemistry, or biology) (*). In addition, applicants must have studied a wide range of ocean-related academic fields and have an active attitude to tackle new challenges.
(*) Regarding mathematics, Mathematics I, Mathematics II, Mathematics A, Mathematics B, Mathematics C
For physics, basic physics, physics
For chemistry, Basic Chemistry, Chemistry
For biology, basic biology, biology
Possess the broad-based attitude necessary to tackle various ocean-related issues.
Possess an attitude of thinking independently, communicating in order to collaborate with diverse people involved in ocean observation and ocean utilization, and understanding and respecting different ways of thinking and cultures. In addition, students must have the basic language skills to carry out academic activities globally.
The following selection process will be conducted to determine the necessary background and ability to receive education in this department.
In the general selection (first period), in order to select those who have acquired a wide range of basic academic abilities, applicants will be judged based on their overall score on the common university entrance test and individual academic ability tests (mathematics and science). In the general selection (later period), in order to select those who have not only basic academic ability but also the ability to develop ideas logically and express them appropriately, the overall score of the common university entrance test and individual academic ability test (essay) is selected. Judge by.
We will evaluate your interest in the academic field of the department, your desire to learn, and the academic ability necessary for learning through essays, interviews, statements of purpose, and research papers.
We will evaluate your interest in the academic field of the department, your desire to learn, and the academic ability necessary for learning through essays, interviews, statements of purpose, and research papers.
We will evaluate your interest in the academic field of the department, your desire to learn, and the academic ability necessary for learning through individual academic ability tests, interviews, results of the EJU, statement of reasons for application, and transcripts.