1. Policy for organizing the curriculum
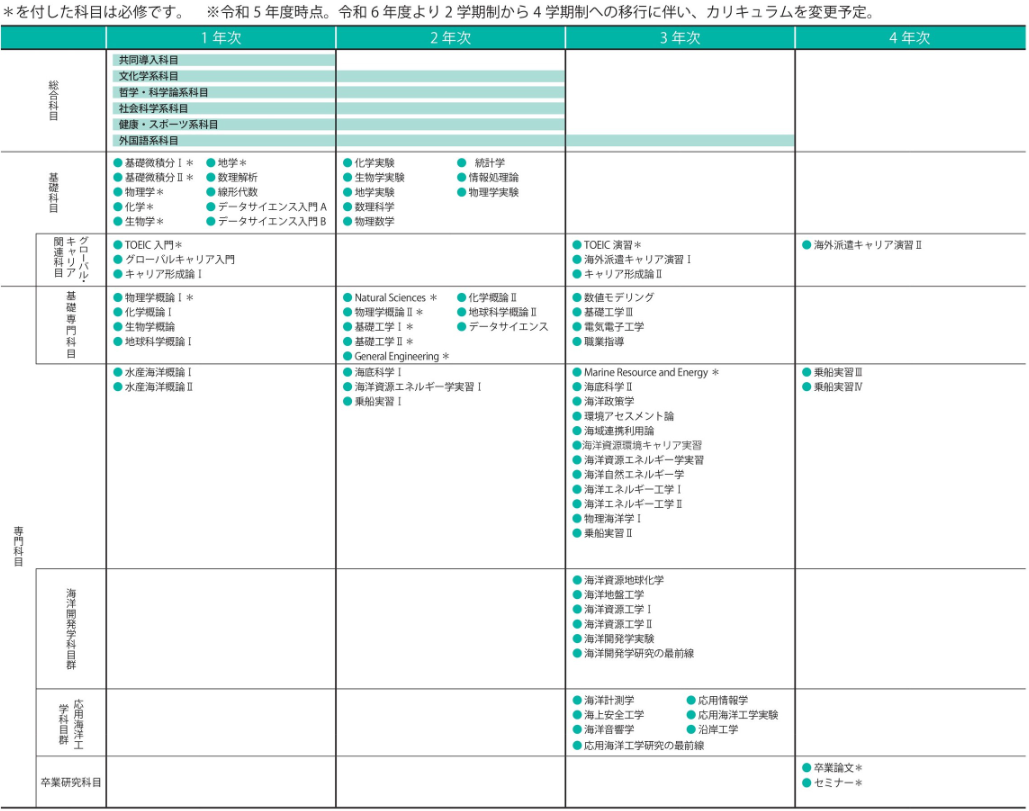
In the Department of Marine Resources and Energy, we offer ``General Subjects,'' ``Introductory Subjects,'' ``Basic Specialized Subjects,'' and ``Specialized Subjects,'' in order to help students acquire the four basic skills and abilities listed in ``2'' below. We will systematically organize ``subjects'' and ``global career-related subjects.'' Furthermore, in order to facilitate cross-disciplinary study of specialized subjects, we will organize a wide range of content related to the sustainable development and use of marine resources and energy into ``specialized subjects.''
2. Policies regarding educational content and educational implementation methods
Class subjects are divided into ``general subjects,'' ``specialty introductory subjects,'' ``basic specialized subjects,'' ``specialized subjects,'' and ``global career-related subjects,'' with lectures and exercises. , conduct experiments and practical training.
(1)Specialized knowledge
From the 1st year to the 3rd year, we aim to help students acquire basic and specialized knowledge on a wide range of basic science related to the ocean, the development and use of ocean resources and renewable energy, the conservation, restoration, and impact assessment of the marine environment. Basic specialized courses are held in each year, and specialized courses are mainly held in the second and third years.
(2) Rich internationality and wide-ranging education
We offer "general subjects" to help students acquire communication skills, including language skills, presentation skills, and a high level of international and cultural awareness. In order to help students acquire basic knowledge of natural science and mathematical science, as well as basic information technology, which are the foundation for learning specialized subjects, we offer ``specialized introductory subjects'' in the first and second years. We will implement it. In order to equip students with the knowledge and ability to respond to international issues related to the ocean, we offer part of the "basic specialized subjects" in the second year and the "specialized subjects" in the second and third years. Lectures will be held in English for some parts of the course.
(3) Ability to think and make decisions independently
In order to acquire the foundation and ability to think logically and make accurate judgments based on a variety of information, we provide exercises, experiments, practical training, and A 4th year seminar and graduation thesis will be held. Furthermore, in order to help students acquire the ability to make ethical decisions, we provide education related to researcher ethics as part of the fourth-year seminar.
(4) Practical skills that can be used in the field
We will utilize the specialized knowledge, information technology, and skills gained through lectures, exercises, experiments, and practical training in ``general subjects,'' ``specialist introductory subjects,'' ``basic specialized subjects,'' and ``specialized subjects.'' In order to comprehensively acquire the knowledge, ability, and ability to proactively and practically explore, solve, and act on various problems in the field from a big-picture perspective, we aim to Learn the basics including practical training, conduct a seminar and graduation thesis in the fourth year, and develop the ability to discover issues that need to be solved, plan a path to a solution, and carry out and verify plans based on the plan. We aim to foster the development of In addition, we offer ``Global Career-related Subjects'' to help students connect smoothly with the international community, industry, and other societies.
3. Policy regarding evaluation method of learning outcomes
In all subjects, learning outcomes and achievement of goals will be rigorously evaluated through exams, reports, presentations, etc.